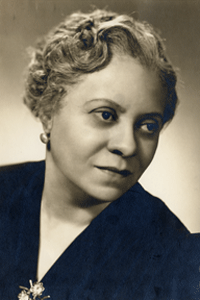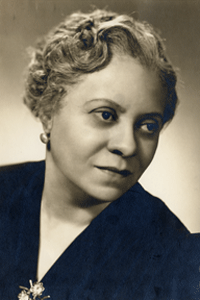 Outside the William Grant Still Ballroom at Robinson Center is an atrium named for Florence Price. It is fitting that these two childhood friends should be memorialized in adjoining spaces.
Outside the William Grant Still Ballroom at Robinson Center is an atrium named for Florence Price. It is fitting that these two childhood friends should be memorialized in adjoining spaces.
Florence Price was the first African-American female composer to have a symphonic composition performed by a major American symphony orchestra. She was born in Little Rock on April 9, 1887, to James H. Smith and Florence Gulliver Smith. Her father was a dentist in Little Rock, while her mother taught piano and worked as a schoolteacher and a businesswoman.
As a child, Smith received musical instruction from her mother, and she published musical pieces while in high school. She attended Capitol Hill School in Little Rock, graduating as valedictorian in 1903. Smith then studied at the New England Conservatory of Music in Boston, Massachusetts, In 1907, she received degrees as an organist and as a piano teacher.
After graduation, Smith returned to Arkansas to teach music. After stints in Cotton Plant, North Little Rock and Atlanta, GA, Smith returned to Little Rock in 1912 to marry attorney Thomas Jewell Price on September 25, 1912. Her husband worked with Scipio Jones.
While in Little Rock, Price established a music studio, taught piano lessons, and wrote short pieces for piano. Despite her credentials, she was denied membership into the Arkansas State Music Teachers Association because of her race.
The Prices moved to Chicago, Illinois, in 1927. There, Price seemed to have more professional opportunity for growth despite the breakdown and eventual dissolution of her marriage. She pursued further musical studies at the American Conservatory of Music and Chicago Musical College and established herself in the Chicago area as a teacher, pianist, and organist. In 1928, G. Schirmer, a major publishing firm, accepted for publication Price’s “At the Cotton Gin.” In 1932, Price won multiple awards in competitions sponsored by the Rodman Wanamaker Foundation for her Piano Sonata in E Minor, a large-scale work in four movements, and her more important work, Symphony in E Minor.
The latter work premiered with the Chicago Symphony Orchestra on June 15, 1933, and the orchestras of Detroit, Michigan; Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania; and Brooklyn, New York, performed subsequent symphonic works by Price. This was the first time a black woman had presented her work on such a stage. In this regard,
Price’s art songs and spiritual arrangements were frequently performed by well-known artists of the day. For example, contralto Marian Anderson featured Price’s spiritual arrangement “My Soul’s Been Anchored in the Lord” in her famous performance on the steps of the Lincoln Memorial in Washington DC on Easter Sunday, April 9, 1939. European orchestras later played Price’s works.
This national and international recognition made her more popular back home, and in 1935, the Alumni Association of Philander Smith College in Little Rock sponsored Price’s return to Arkansas, billing her as “noted musician of Chicago” and presenting her in a concert of her own compositions at Dunbar High School.
In her lifetime, Price composed more than 300 works, ranging from small teaching pieces for piano to large-scale compositions such as symphonies and concertos, as well as instrumental chamber music, vocal compositions, and music for radio. Price died in Chicago on June 3, 1953, while planning a trip to Europe.
 Charlotte Andrews Stephens was the first African American teacher in the Little Rock School District. Between 1910 and 1912, when an elementary school for African Americans was named after her, she became the first woman to have a public building in Little Rock named after her. For nearly fifty years, Stephens Elementary (which is now in its third building) would be the only LRSD building named after a woman.
Charlotte Andrews Stephens was the first African American teacher in the Little Rock School District. Between 1910 and 1912, when an elementary school for African Americans was named after her, she became the first woman to have a public building in Little Rock named after her. For nearly fifty years, Stephens Elementary (which is now in its third building) would be the only LRSD building named after a woman.